|

|

|

|
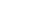
Defining Email Policies > Antispoofing tab > Spoofed Message Detection
|


|

|

|

|
Defining Email Policies > Antispoofing tab > Spoofed Message Detection
|
|
|
Messages that spoof internal domains are from forged addresses that appear to come from users within your organization. Internal domain validation uses Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) authentication, as well as checking the sender's IP address against those configured as outbound routes in the policy.
|
|
|
Messages that spoof external domains are from forged addresses that appear to come from legitimate external organizations. External domain validation uses Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) authentication.
|
|
|
Quarantine. This is the default option. Spoofed messages are kept in quarantine for up to 30 days.
|
|
|
Discard. Spoofed messages are discarded.
|
|
|
Tag subject with. The subject line of detected spoofed messages are tagged with "SPOOFED:" or a custom tag that you enter.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
|
|
Select the Domains tab to add allowed sender domain names, for example "forcepoint.com".
|
|
|
Select the IP Addresses tab to add allowed sender IP addresses, either as a list of individual addresses, or address blocks in CIDR notation (for example, 10.10.10.8/30). List entries are separated by a line break.
|
|
3.
|
Click Add to enter a new domain or list of IP addresses. You can add multiple domains or addresses, and you can add a combination of domain names and/or IP addresses if required.
|
|
5.
|
|
|
Use DMARC policy. This is the default option. Spoofed messages will be quarantined or rejected, depending upon the domain owner's policy.
|
|
|
Quarantine. Spoofed messages are kept in quarantine for up to 30 days.
|
|
|
Discard. Spoofed messages are discarded.
|
|
|
Tag subject with. The subject line of detected spoofed messages are tagged with "SPOOFED:" or a custom tag that you enter.
|
|
|
When the Action is Use DMARC policy, Quarantine, or Tag Subject, the alternative option is Tag Subject.
|
|
|

|

|

|

|
Defining Email Policies > Antispoofing tab > Spoofed Message Detection
|